|
Diagram from EctopicPregnancyFoundation.org |
By Susan Dammann, RN, Medical Specialist
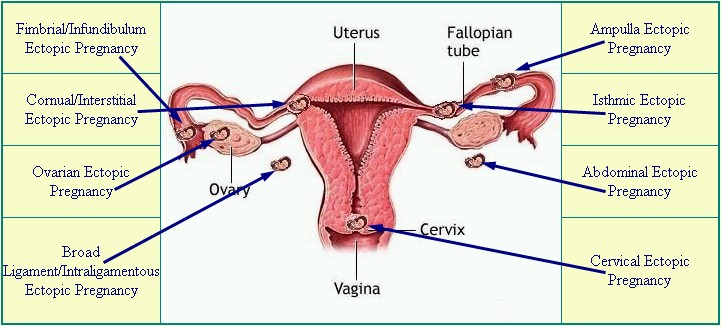
Ectopic pregnancies occur in a range of 1 in 40 to 1 in 100 pregnancies. An ectopic pregnancy is any pregnancy that implants somewhere outside of the uterus, most often occurring in one of the fallopian tubes, which is also known as a tubal pregnancy. Other locations for an ectopic pregnancy include the ovary, the cervix, and the abdominal cavity.
Ectopic pregnancies are life-threatening for the mother, and the baby (embryo) cannot survive. Ectopic pregnancies may occur with or without the use of birth control.
Though rare when considered with the overall number of U.S. pregnancies, ectopic pregnancies still occur at a rate of 100,000 per year, according to the Center for Disease Control. The CDC also reports the life-threatening nature of an ectopic pregnancy for a mother: "Ectopic pregnancies are the leading cause of pregnancy related deaths in the first trimester and account for 9% of all pregnancy related deaths in the country."
Causes
An ectopic pregnancy can result from any condition blocking or slowing the movement of the embryo through the fallopian tube, where it then becomes lodged. The cause, sometimes unknown in an individual case, may include any of the following:
- Tubal damage resulting from sexually transmitted infections
- Inflamed, damaged or misshapen fallopian tube
- Hormonal imbalances
- Abnormal fetal development
- Complications/scarring after a ruptured appendix
- Endometriosis
- A previous ectopic pregnancy
- Scarring from past infections or surgery of the female organs
- Illicit drug use (“An alarming increase in ectopic pregnancy-related deaths among Florida women is likely caused by illicit drug use and delays in seeking medical care…”)
Risk Factors
- Having had many sexual partners
- Surgery to reverse a tubal ligation
- IUD in place
- In vitro fertilization
- Over 35 years of age
- Some infertility treatments
- Tubal ligation (more likely 2 or more years after the procedure)
Symptoms
Initially, an ectopic pregnancy may not cause any symptoms outside of those of a normal pregnancy. A pregnancy test will read positive, but will likely be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding—heavy vaginal bleeding is not likely unless the ectopic pregnancy is in the cervix
- Pain in the lower belly or pelvic area
- No period
- Low back pain
- Cramping on one side of the pelvis
If the areas around the ectopic pregnancy rupture and bleed, symptoms may worsen and include:
- Low blood pressure
- Pain in the shoulder area, due to blood leaking from the fallopian tube
- Urge to have a bowel movement, due to blood leaking from the fallopian tube and pooling
- Severe, sharp, and sudden pain in the lower abdomen
- Fainting or feeling faint
Complications
- Unless treated, a ruptured fallopian tube may be life-threatening
- Shock
- Infertility
Diagnosis
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, the physician may do a pelvic exam to check for pain. Tenderness or a mass in the fallopian tube or ovary may be an indicator. Blood tests and vaginal ultrasound exam help confirm the diagnosis, as does checking hCG blood levels over 1 to 2 days.
[Related—Transvaginal Sonogram: Is it Necessary in Your Center?]
Ectopic pregnancy may occur after tubal ligation, even more so if the woman was sterilized before 30 years of age. One study found these women were twice as likely to have a subsequent ectopic pregnancy as those women who undergo tubual ligation after the age of 30. It should never be assumed that a woman’s history of tubal ligation automatically rules out the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment
In order to prevent the loss of a mother’s life in addition to the loss of her embryo, intervention is required. The pregnancy cannot continue to full-term. If the ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed before symptoms occur, treatment may consist of an injection of methotrexate to stop cell growth. Ectopic pregnancies can be removed through laparoscopic surgery. If the fallopian tube is damaged, it may need to be removed as well.
Emergency medical attention is required if the fallopian tube has ruptured and heavy bleeding is occurring. Emergency surgery (laparotomy) may be required to stop the blood loss, as well as the termination of the pregnancy and possibly removal of the fallopian tube. Because the rupture can lead to shock, the following may be necessary:
- Blood transfusion
- Intravenous fluids
- Oxygen
- Trendelenberg position
- Added warmth
Prognosis
While some women do not conceive subsequent to an ectopic pregnancy, approximately one-third do experience a later pregnancy. Of this one-third who do become pregnant following an ectopic pregnancy, approximately one-third will have a repeat ectopic pregnancy.
Prevention
The best means of avoiding a tubal pregnancy is to avoid anything that would cause infection, or scarring of the fallopian tubes. Early diagnosis and treatment of all STD/STIs is critical. There are, however, no preventative measures to avoid ectopic pregnancy occurring outside the fallopian tubes.
Patient Instruction Sheet
This information is critical for pregnancy center staff to know. With every client who comes in our center with a positive pregnancy test we must be aware that she could potentially have an ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, it is recommended every center have a policy and procedure for advising clients of the signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
This could be as simple as giving your client a sheet of instructions and information listing the signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, along with instruction to contact a health professional immediately if she experiences any of these symptoms.
Sources:
1. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/ectopic-pregnancy/DS00622
2. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000895.htm
3. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001897/
Tubal pregnancy; Cervical pregnancy; Tubal ligation-ectopic pregnancy
4. CDC Fact Sheet: Ectopic Pregnancy Risk after Tubal Sterilization
[CDC Reproductive Health Information Source, 7/04 http://pregnancy.about.com/cs/ectopicpregnancy/l/bltubalfacts.htm]
5. http://health.usnews.com/health-news/news/articles/2012/02/16/illicit-drug-use-may-be-driving-rise-in-ectopic-pregnancies-in-florida